Image 1 of 1
Image 1 of 1


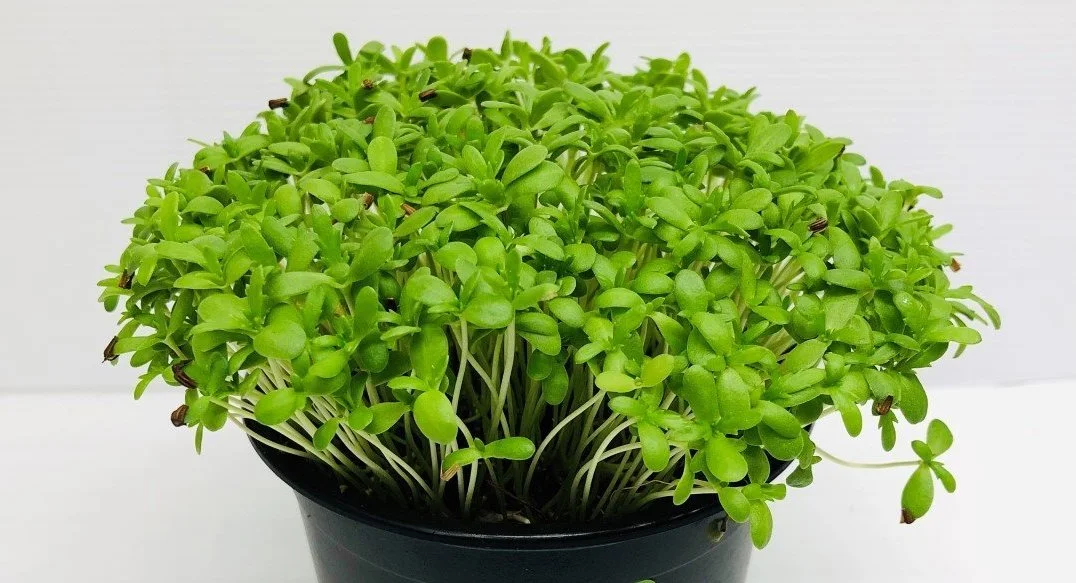
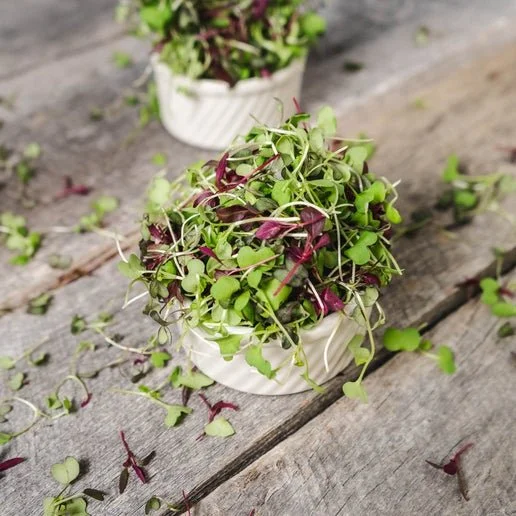
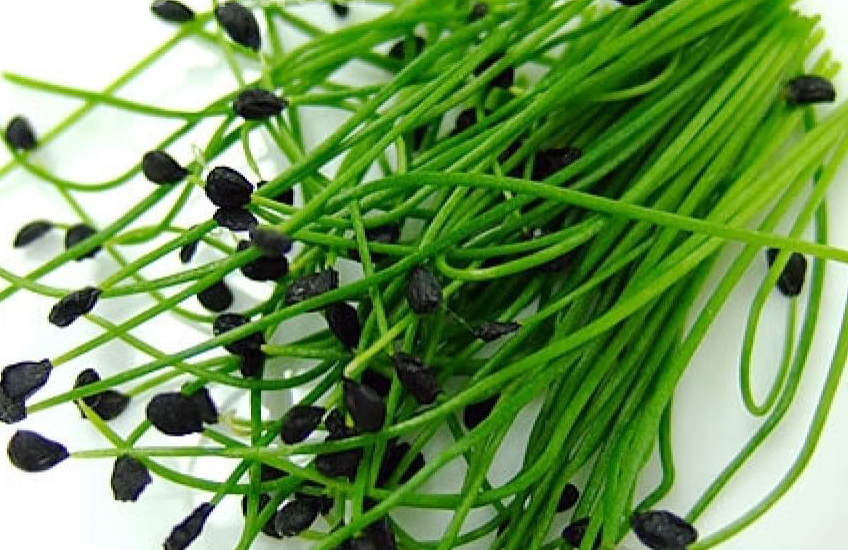
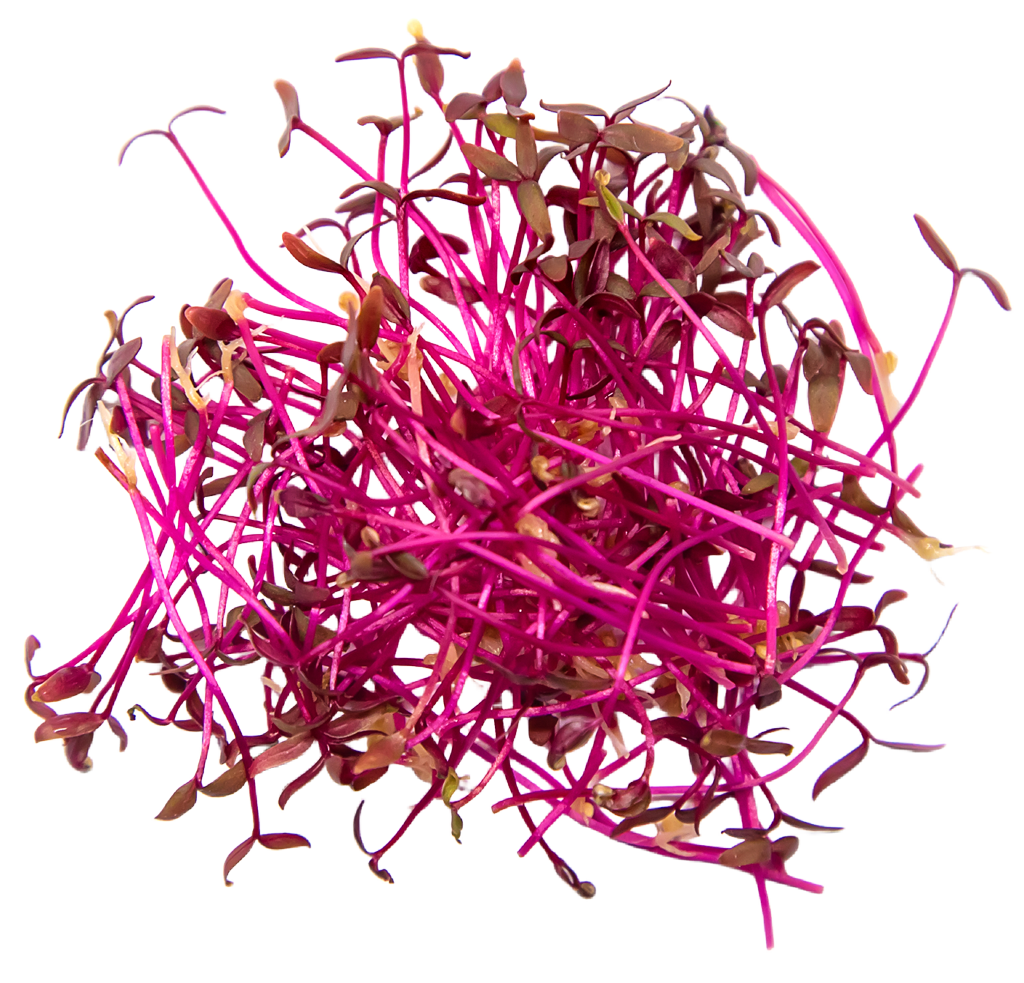
Sweet Lupine Microgreens (1oz)
History:
Sweet lupine's history traces back to ancient consumption in the Mediterranean and Latin America, but modern, low-alkaloid "sweet" varieties were first bred in Germany in the 1920s and 1930s. This breakthrough transformed lupine from a bitter, often toxic plant primarily used for animal feed or requiring extensive soaking, into a valuable, sustainable food crop with high protein content. These sweet varieties, such as Lupinus albus (white lupine), Lupinus angustifolius (narrow-leafed lupine), and Lupinus luteus (yellow lupine), are now a significant crop in countries like Australia and are increasingly used in human food products.
Flavor Profile:
Sweet lupine microgreens have a mild, nutty, and umami flavor, with a crisp and juicy texture and a slightly floral aftertaste. They are a versatile addition to dishes, tasting similar to sunflower or pea shoots and providing a gentle sweetness and savory depth.
Uses:
Sweet lupine microgreens can be used as a flavorful and nutritious garnish for a wide range of dishes, including salads, sandwiches, wraps, soups, and gourmet plates. Their mild, nutty flavor and crisp texture add a unique element to both cold and hot preparations, and their visual appeal makes them ideal for enhancing a dish's aesthetic. They can also be blended into smoothies for a protein boost.
Salads and bowls: Add a nutty crunch to fresh greens and grain bowls.
Sandwiches and wraps: Enhance the taste and texture of gourmet sandwiches and wraps.
Garnishes: Use for fine dining and plating to add a striking visual contrast to main courses.
Soups and hot dishes: Sprinkle on top of hot dishes just before serving for a refreshing bite.
Smoothies: Blend into smoothies to increase their protein content.
Desserts: Incorporate into desserts for an added layer of flavor and texture.
Nutrition:
Sweet lupine microgreens are rich in protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They are an excellent source of plant-based protein, iron, potassium, and vitamins like C and B vitamins. Additionally, they are packed with beneficial compounds such as sulforaphane, and antioxidants.
Protein: Lupine microgreens are a high-protein plant-based food source, beneficial for vegan and vegetarian diets.
Fiber: They contain dietary fiber, which supports digestive health.
Healthy Fats: They provide unsaturated fatty acids, including omega-3s, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins: Rich in vitamins C and some B vitamins. Some varieties may also be high in vitamins A and E.
Minerals: Excellent source of minerals such as iron, potassium, zinc, and copper.
Other beneficial compounds
Antioxidants: They contain antioxidants, which help protect the body from damage.
Sulforaphane: Contain sulforaphane, a compound known for its protective properties.
Health Benefits:
Sweet lupine microgreens are nutrient-dense, offering high protein, fiber, and vitamins A and C, while also being rich in sulforaphane and omega-3 fatty acids. These microgreens support eye and immune health, promote gut health, and may help with blood sugar management and cardiovascular health. Their high fiber and protein content contribute to satiety, and they are a good source of antioxidants that can help combat chronic inflammation.
High in protein: A fantastic plant-based protein source, ideal for vegan diets.
Rich in fiber: Supports digestive and gut health and can increase feelings of fullness.
Good source of vitamins: Contain significant amounts of vitamin A and beta-carotene for eye health and immune function, as well as vitamin C and B vitamins.
Antioxidant-rich: Contain sulforaphane and other antioxidants that may help protect against chronic inflammation and related diseases.
Healthy fats: High in unsaturated fatty acids, including omega-3s, which are beneficial for cardiovascular health and gut microbiota.
Mineral content: A good source of minerals like iron, potassium, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, and zinc.
Potential health impacts
Supports gut health: The fiber in lupine microgreens can positively influence gut bacteria, potentially reducing the risk of colorectal cancer.
Aids blood sugar and cholesterol control: Their low glycemic index and unique proteins may help improve insulin sensitivity and manage blood glucose levels. They have also been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol.
Promotes cardiovascular health: Their high levels of omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and beneficial phytochemicals may help lower blood pressure and improve blood lipids.
Contributes to satiety: The combination of high protein and fiber can help you feel fuller for longer, which can aid in weight management.
Eye health: The presence of antioxidants like beta-carotene and lutein can help protect your vision.
History:
Sweet lupine's history traces back to ancient consumption in the Mediterranean and Latin America, but modern, low-alkaloid "sweet" varieties were first bred in Germany in the 1920s and 1930s. This breakthrough transformed lupine from a bitter, often toxic plant primarily used for animal feed or requiring extensive soaking, into a valuable, sustainable food crop with high protein content. These sweet varieties, such as Lupinus albus (white lupine), Lupinus angustifolius (narrow-leafed lupine), and Lupinus luteus (yellow lupine), are now a significant crop in countries like Australia and are increasingly used in human food products.
Flavor Profile:
Sweet lupine microgreens have a mild, nutty, and umami flavor, with a crisp and juicy texture and a slightly floral aftertaste. They are a versatile addition to dishes, tasting similar to sunflower or pea shoots and providing a gentle sweetness and savory depth.
Uses:
Sweet lupine microgreens can be used as a flavorful and nutritious garnish for a wide range of dishes, including salads, sandwiches, wraps, soups, and gourmet plates. Their mild, nutty flavor and crisp texture add a unique element to both cold and hot preparations, and their visual appeal makes them ideal for enhancing a dish's aesthetic. They can also be blended into smoothies for a protein boost.
Salads and bowls: Add a nutty crunch to fresh greens and grain bowls.
Sandwiches and wraps: Enhance the taste and texture of gourmet sandwiches and wraps.
Garnishes: Use for fine dining and plating to add a striking visual contrast to main courses.
Soups and hot dishes: Sprinkle on top of hot dishes just before serving for a refreshing bite.
Smoothies: Blend into smoothies to increase their protein content.
Desserts: Incorporate into desserts for an added layer of flavor and texture.
Nutrition:
Sweet lupine microgreens are rich in protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They are an excellent source of plant-based protein, iron, potassium, and vitamins like C and B vitamins. Additionally, they are packed with beneficial compounds such as sulforaphane, and antioxidants.
Protein: Lupine microgreens are a high-protein plant-based food source, beneficial for vegan and vegetarian diets.
Fiber: They contain dietary fiber, which supports digestive health.
Healthy Fats: They provide unsaturated fatty acids, including omega-3s, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins: Rich in vitamins C and some B vitamins. Some varieties may also be high in vitamins A and E.
Minerals: Excellent source of minerals such as iron, potassium, zinc, and copper.
Other beneficial compounds
Antioxidants: They contain antioxidants, which help protect the body from damage.
Sulforaphane: Contain sulforaphane, a compound known for its protective properties.
Health Benefits:
Sweet lupine microgreens are nutrient-dense, offering high protein, fiber, and vitamins A and C, while also being rich in sulforaphane and omega-3 fatty acids. These microgreens support eye and immune health, promote gut health, and may help with blood sugar management and cardiovascular health. Their high fiber and protein content contribute to satiety, and they are a good source of antioxidants that can help combat chronic inflammation.
High in protein: A fantastic plant-based protein source, ideal for vegan diets.
Rich in fiber: Supports digestive and gut health and can increase feelings of fullness.
Good source of vitamins: Contain significant amounts of vitamin A and beta-carotene for eye health and immune function, as well as vitamin C and B vitamins.
Antioxidant-rich: Contain sulforaphane and other antioxidants that may help protect against chronic inflammation and related diseases.
Healthy fats: High in unsaturated fatty acids, including omega-3s, which are beneficial for cardiovascular health and gut microbiota.
Mineral content: A good source of minerals like iron, potassium, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, and zinc.
Potential health impacts
Supports gut health: The fiber in lupine microgreens can positively influence gut bacteria, potentially reducing the risk of colorectal cancer.
Aids blood sugar and cholesterol control: Their low glycemic index and unique proteins may help improve insulin sensitivity and manage blood glucose levels. They have also been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol.
Promotes cardiovascular health: Their high levels of omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and beneficial phytochemicals may help lower blood pressure and improve blood lipids.
Contributes to satiety: The combination of high protein and fiber can help you feel fuller for longer, which can aid in weight management.
Eye health: The presence of antioxidants like beta-carotene and lutein can help protect your vision.